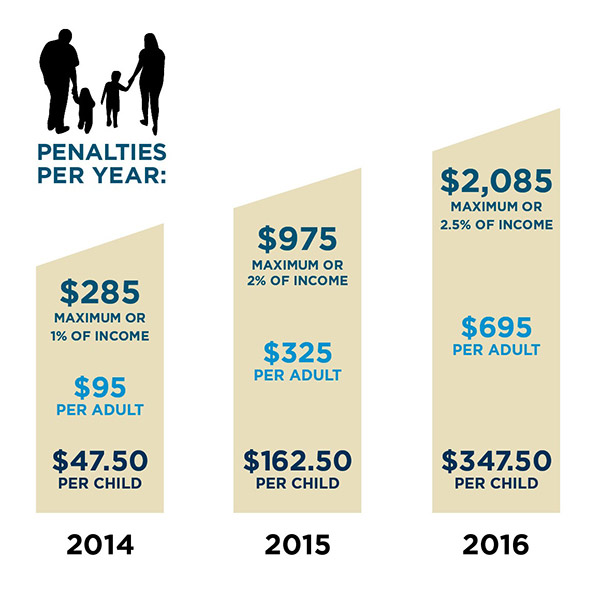
An HSA a tax-favored savings account that is utilized in combination with a high deductible medical insurance strategy. The cash in the account helps pay the deductible in addition to any other qualified medical expensesincluding coinsurancethat may not be covered by the plan once the deductible has been fulfilled. An HSA resembles a private retirement account (Individual Retirement Account), because it too can be bought a range of investment cars, while building up tax-free interest.
The list below requirements should be satisfied: Minimum deductible: $1,250 person; $2,500 household Out-of-pocket maximum (includes deductible): $5,000 person; $10,000 family No services spent for prior to satisfying deductible (other than for preventive care) No deductible needed for preventive care For household coverage: household deductible must be met prior to any compensation can be made No prescription drug copayments Higher limits permitted non-participating service provider services.
,, what? Common medical insurance terms you need to know, however no one ever explained. Prior to you can select the best health insurance strategy for yourself, your family or your company, you require to familiarize yourself with some typical health insurance terms. Below is a glossary of commonly used health care terminology in the insurance market.
Let's begin by addressing a few of the more common medical insurance terminology concerns: A is the amount of money you pay an insurance coverage service provider for healthcare protection under a particular medical insurance policy. For the most part, premiums do not count towards fulfilling your deductible. If the yearly premium is $2,700 for the strategy you select, you will pay $225 per month to the insurance coverage supplier for the healthcare protection offered under the policy.
The 20-Second Trick For How To Get Health Insurance After Open Enrollment
If you have a $3,500 deductible, you will be accountable for paying the first $3,500 of medical expenses out-of-pocket every year, before your insurance coverage company starts to cover a percentage of the bill. A is a flat quantity you must pay out-of-pocket for a covered service. For the most part, copays do not count towards meeting your deductible. how much is long term care insurance.
is the percentage of medical payments you are accountable for paying out-of-pocket after your deductible is satisfied. Your insurance provider will pay the staying portion. If you have a 20% coinsurance, your insurance company will pay 80% of covered medical costs after your deductible is satisfied, and you will pay the remaining 20% out-of-pocket.
Keep in mind: Check your medical insurance policy to see exactly which out-of-pocket payments are counted towards your out-of-pocket maximum. If your annual out-of-pocket optimum is $3,000, you will no longer be needed to pay coinsurance for the remainder of the year after you make an overall of $3,000 in certifying, yearly out-of-pocket payments.
The enabled amount is normally lower than the supplier's standard rate and is the maximum an in-network supplier is allowed to charge for a covered service.: The health related services or products covered by a health insurance coverage policy (see: covered services). Obama care plans need to all cover 10 minimum essential health advantages.
Facts About How Do I Get Health Insurance Uncovered
A demand sent to the insurance provider detailing the health services rendered and requesting payment from the business for those services. Claims might be submitted directly by the doctor to the insurance company (this is typically the case) or by the patient. Covered services: Healthcare services, prescription drugs and medical devices that are covered by your healthcare plan.: Medical treatments, health services or products not covered by a health insurance coverage plan, such as cosmetic surgery.: A set of 10 health care benefits established by the Affordable Care Act that all insurance providers should use on all insurance coverage plans.: An income level set each year by the Federal federal government that is utilized as a threshold when determining eligibility for certain federal government services.: A list of prescription medications an insurance coverage will cover, including both name-brand and generic https://timesharecancellations.com/are-you-ready-to-cancel-your-timeshare-we-may-be-able-to-help/ drugs.: Tax-exempt savings accounts utilized to spend for health care costs connected with qualifying high deductible insurance coverage plans.
You will pay lower rates when using an in-network supplier than an out-of-network provider. The maximum amount an insurer will pay for advantages throughout your life time. Changes to healthcare under Obama no longer permit insurance companies to set life time optimums for "important" health services. Annual Open enrollment: The time period you have for registering for health insurance coverage.
Some medical insurance prepares need a referral from a PCP in order for visits to specialized providers to be covered (see: specialized service provider).: A minimal window, normally 60-days, during which those who experience specific certifying life occasions can enroll in health insurance outside of the Yearly Open Enrollment Period. Specialized providers concentrate on (or focus on) a specific branch of medicine.
Health care strategies often have higher copays for visits to specialized service providers and need referrals from medical care doctors prior to specialty services are covered (see: primary care provider). When a health problem or injury requires instant care but is not harmful. Check outs to immediate care facilities generally happen outside of normal doctor business hours, or in cases where a timely consultation is not readily available.
How How To Fight Insurance Company Totaled Car can Save You Time, Stress, and Money.
Disclaimer: This is only a short list of health insurance terminology, and is not all-inclusive. The precise meanings for the medical insurance terms above might vary from the terms and definitions provided in your medical insurance policy. This glossary is implied to be instructional in nature and does not supersede policy-specific health insurance coverage terms or meanings.
Your medical insurance deductible and your monthly premiums are probably your two largest healthcare costs. Even though your deductible counts for the lion's share of your health care spending budget plan, understanding what counts toward your medical insurance deductible, and what doesn't, isn't simple. The design of each health plan identifies what counts towards the medical insurance deductible, and health insurance designs can be infamously made complex.
Even the very same plan may alter from one year to the next. You need to read the small print and be savvy to understand what, precisely, you'll be anticipated to pay, and when, precisely, you'll need to pay it. Mike Kemp/ Getty Images Money gets credited towards your deductible depending on how your health insurance's cost-sharing is structured.
Your medical insurance may not pay a cent toward anything but preventive care until you've fulfilled your deductible for the year. Prior to the deductible has been satisfied, you spend for 100% of your medical expenses. After the deductible has been met, you pay only copayments (copays) and coinsurance up until you fulfill your strategy's out-of-pocket optimum; your medical insurance will select up the remainder of the tab.
Things about How Much Does An Eye Exam Cost Without Insurance
As long as you're utilizing medical service providers who become part of your insurance coverage strategy's network, you'll just need to pay the amount that your insurance provider has actually worked out with the providers as part of their network arrangement. Although your medical professional may bill $200 for a workplace see, if your insurance provider has a network agreement with your doctor that requires office visits to be $120, you'll only need to pay $120 and it will count as paying 100% of the charges (the physician will have to cross out the other $80 as part of their network contract with your insurance plan).